Fiber Optics Test
For
a profile parameter (α)=1, the profile shape of refractive index for a graded
index fiber will be _____________.
a.
triangular
b.
parabolic
c. step
d.
circular
SOLITON
is a/an _____________.
a.
type of optical fiber
b.
optical source
c.
optical detector
d.
pulse traveling in optical fiber
The
fiber gyroscope is an _____________.
a.
Intrinsic fiber sensor
b.
Interferometer fiber sensor
c.
Extrinsic fiber sensor
d.
Extinction fiber sensor
The
output power of a LASER is greater than that of a LED because of _____________.
a.
stimulated emission
b.
spontaneous emission
c.
straight emission
d. None
of the above
A
multimode graded index fiber exhibits total pulse broadening of 0.2 µsec over a
distance of 10Km. Estimate the maximum possible bandwidth assuming that there
is no inter-symbol interference.
a. 5
MHZ
b. 2.5
MHZ
c.
10 MHZ
d. 1
MHZ
Dispersion
is low in the _____________.
a.
Multimode step index fiber
b.
Single mode step index fiber
c. Two
mode step index fiber
d. None
of the above
For
an ideal photo detector, the absorption coefficient must be _____________.
a. low
b. zero
c. one
d.
large
This
question is based upon the figure shown below
For
a step index fiber, relationship between numerical aperture (NA) and coupling
efficiency (ηc) is _____________.
a. a
b. b
c. c
d. d
Optical
bandwidth (OB) relates to electrical bandwidth (EB) when
a.
OB<EB
b.
OB=EB
c.
OB>EB
d.
OB≥EB
Superluminescent
LED's are preferred because of _____________.
a.
large spectral linewidth
b. a
directional output beam
c.
low output power
d.
small size
Germanium
photodiodes are generally not preferred in the optical fiber system because of
_____________.
a.
large current gain
b.
large voltage gain
c.
temperature dependence
d.
large dark current
The
refractive index is defined as the ratio of _____________.
a. the
velocity of light in a vacuum to the velocity of light in the medium
b.
the velocity of light in the medium to the velocity of sound in a vacuum
c. the
velocity of light in the medium to the velocity of light in a vacuum
Dispersion
is the lowest in a _____________.
a.
Multimode step-index fiber
b.
Multimode graded-index fiber
c.
Single-mode step-index fiber
d.
Silicon fiber
What
would the optical return loss (ORL) be defined as when r-fresnal reflection
occurs at a fiber-air interface?
a. ORL=
-10log10r
b.
ORL= -20log10r
c. ORL=
-30log10r
d. ORL=
-10loger
When
optical power is incident on the photo detector during the 0 bit period, then
the system is said to exhibit _____________.
a. a
non-zero extinction ratio
b. a
zero extinction ratio
c. an
infinity extinction ratio
d. an
infinity absorption ratio
Macro
bending losses in optical fibers can be reduced by designing the fibers with
_____________.
a. a
smaller refractive index difference
b. a
fiber glass
c. a
silica glass
d. a
larger refractive index difference
Which
phenomenon does not let light rays escape an optical fiber?
a.
Total internal reflection
b.
Total internal refraction
c.
Total internal diffraction
d.
Total internal attenuation
Rayleigh
scattering is a _____________.
a.
non-linear scattering
b. differential
scattering
c.
cumulative scattering
d.
linear scattering
IEEE
802.5 is a/an _____________.
a.
Ethernet
b.
Token bus
c.
Token ring
d.
Token star
For
a multimode optical graded index fiber, the profile parameter (α) will be equal
to:
a. ∞
b. Zero
c. 1
d. 2
Scattering
losses happen due to:
a. a
rise in temperature
b.
imperfections in glass manufacturing process
c.
humidity
d.
bending of fiber
Germanium
avalanche photodiodes can be used for _____________.
a.
longer wavelength operation
b.
shorter wavelength operation
c. low
output power operation
d.
minimum noise operation
FDDI
can support a data rate of
a.
10 Mbps
b. 10
Gbps
c. 100
Mbps
d. 1000
Mbps
Which
one of the following is a type of non-linear scattering?
a.
Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS)
b.
Rayleigh scattering
c. Mie
scattering
d.
Ultraviolet scattering
Dark
line defects (DLDs) occur when:
a.
non-radiative electron-hole recombination occurs
b.
mobile impurities are displaced into the active region of LASER
c. all
modes are not stabilized
d. all
modes are not polarized
The
vapor-phase deposition technique is used to produce _____________.
a.
fiber-rich glasses
b.
silica-rich glasses
c.
oxide-rich glasses
d.
carbonate-rich glasses
Light
emitting diodes (LED's) are:
a.
Monochromatic incoherent sources
b.
Monochromatic coherent sources
c.
Incandescent light sources
d.
None of the above
Silicon
reach through avalanche photodiodes has _____________.
a.
maximum absorption of photons
b.
maximum absorption of electrons
c.
maximum quantum efficiency
d.
minimum noise
Surface
emitter LEDs have high radiance because _____________.
a. a
hemisphere of n type GaAs is formed around a diffused p-type region
b. of
p-type diffusion into the n-type substrate
c. it
restricts the emission to a small active region
d.
of n-type diffusion into the p-type substrate
This
question is based upon the figure shown below
What
is signal attenuation in an optical fiber where P1=Input power and P0=Output
power
a. a
b. b
c. c
d. None
of the above
The
cutback technique is a/an _____________.
a.
attenuation measurement technique
b.
refractive index measurement technique
c.
impurity measurement technique
d.
frequency measurement technique
In
p-i-n photodiodes "i" stands for:
a.
Internal
b.
Intrinsic
c.
Impurity
d. None
of the above
What
is the relationship between refractive index (n1) of core and refractive index
(n2) of cladding for an optical fiber?
a. n1
< n2
b. n1 =
n2
c.
n1 <= n2
d. n1
> n2
Graded-index
fibers have:
a. a
constant refractive index in the core
b. a
variable refractive index in the cladding
c. a
variable refractive index in the core
d.
None of these
LED
is more suitable for analog transmission because of its _____________.
a.
linearity
b.
bandwidth (spectrum)
c.
modulation property
d.
output power
Homodyne
detection is used for _____________.
a.
incoherent systems
b.
incandescent systems
c.
coherent systems
d.
analog systems
The
rays which travel in a helical path through an optical fiber are called
_____________.
a.
refracted rays
b.
reflected rays
c.
infra-red rays
d.
skew rays
Mirrors
are placed in LASER optical sources to maintain conditions for _____________.
a.
incoherence
b.
amplification
c.
modulation
d.
coherence
Avalanche
photodiodes are _____________.
a. less
sensitive than simple photodiodes
b.
more sensitive than simple photodiodes
c.
cheaper than simple photodiodes
d. less
complex in structure than simple photodiodes
Dark
spot defects (DSD's) occur in:
a.
Non-semiconductor LASER
b.
Fiber LASER
c.
Glass fiber LASER
d.
Injection LASER
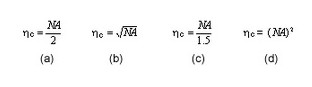

No comments:
Post a Comment